Text link
Text links are lightweight navigational elements. Links can appear within a paragraph, after a paragraph, standalone, or in a list of other links. They are underlined by default.
- CSS
- Marko
- React

Clear
The link text makes it clear where it will take the user.
Identifiable
Links are familiar and easily identifiable amongst other content.
Concise
Link text is short. Aim for fewer than 5 words.
When to use
- Navigating within the app
- Navigating externally
- Navigating to an element on a page (anchor link)
- Email addresses and phone numbers
When not to use
- Actions that manipulate data or how its displayed
- Actions that change state
- Navigating to legal links
Text links vs Link buttons
If an action results in a URL change or new browser tab use a Text link. Everything else is a Button.
Semantics
HTML text links and buttons have important differences in behaviors, interactions and expectations. For example, a Text link will perform its interaction when clicked and when the enter key is pressed. A Button will perform its interaction when clicked and when the enter and spacebar keys are pressed. When holding the control or command key a Text link will open a new browser tab, a Button will not.
Buttons take action, links navigate
- Use a link when you’re navigating to another place, such as: an item page, a seller profile, a page "skip link" etc.
- Use a button when you are performing an action, such as: "bid," "add," "search," etc.
- Text
- Underline
Inline
Inline links appear within paragraphs and sentences. They always have an underline to differentiate between non-link content.
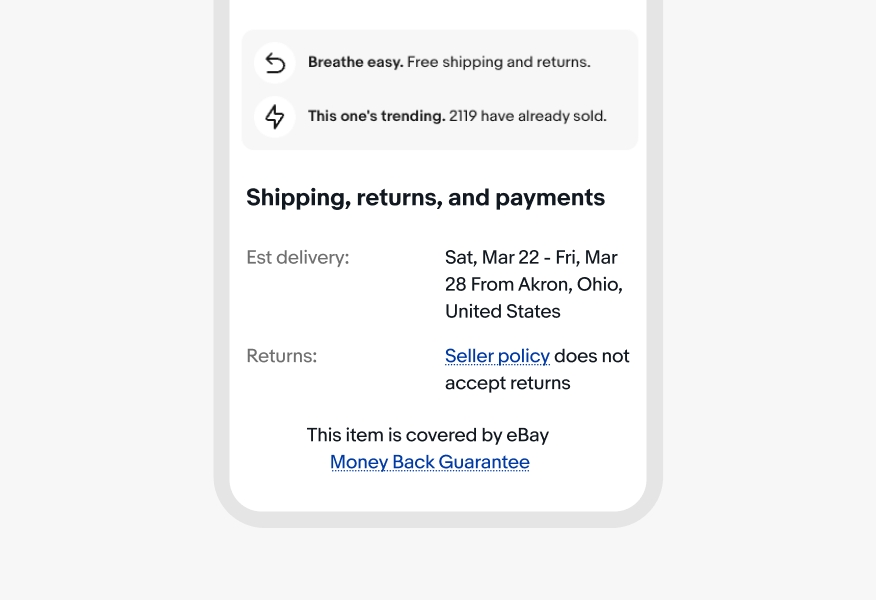
Color
Links should generally match the color of the content around it. Standalone links can use a secondary color within a list to avoid overwhelming the UI or a primary color for more emphasis.
Exception: Legal links must use the specific legal link color.
Size
Text links inherit their size and styling from the content around them.
State
Text links use state layers for interaction states. The available states are enabled, hover, focused, visited, and disabled. Learn more about the state layer color values in Color tokens.
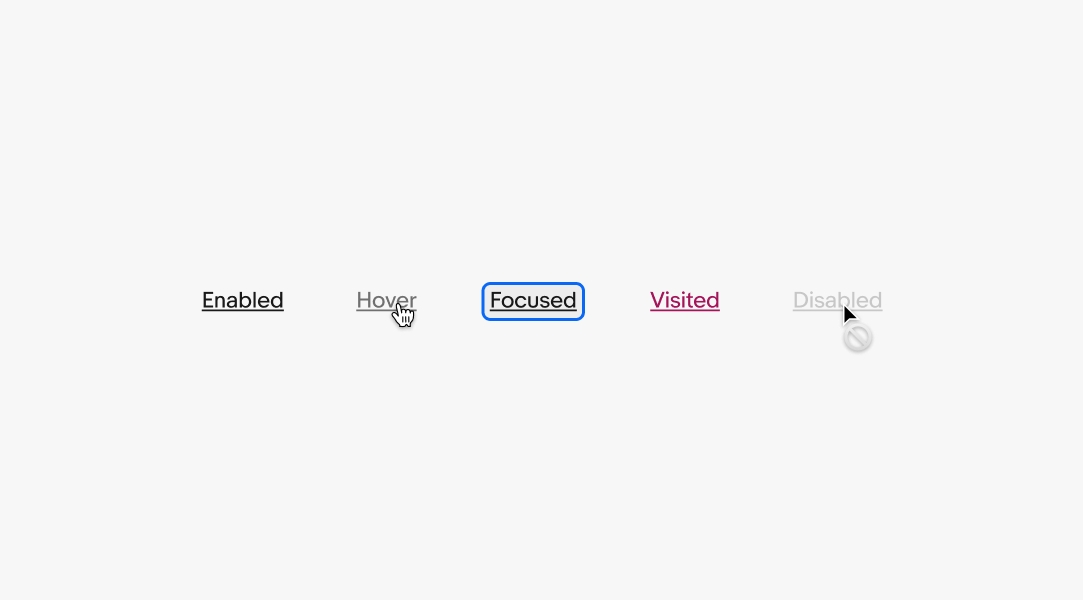
Background
Links placed on backgrounds using our expanded color palette should use the coordinating foreground color to match. This ensures we meet WCAG’s 4.5:1 ratio standard for AA contrast. See Accessibility foundations for more info.
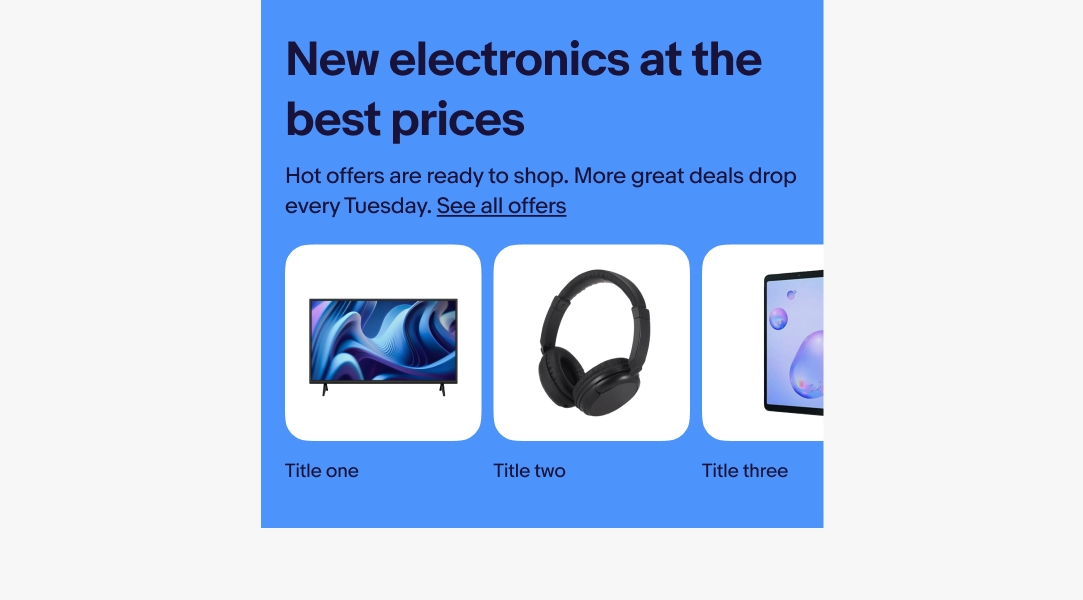
Native
Keep in mind that on native devices, it's common for an entire line of text to be tappable when it contains a link. This is particularly important if multiple links are close together, as it could lead to accidental taps.
Content
Use words that describe where the link leads and what content is expected.

Don’t use ambiguous words like “click here” or “learn more”. They lack necessary context for screen reader users.
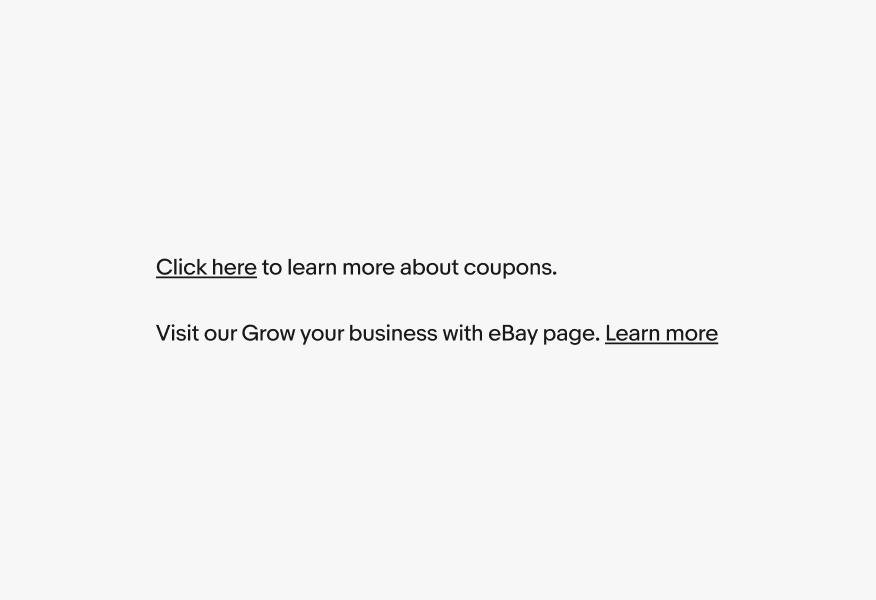
Underline
Always underline links within or right after paragraphs. Only remove the underline where the context is clear, like a list of links in a footer.

Don’t remove the underline for links near other content. This can easily get lost and are inaccessible to low-sight users.

Size
Do use the same type size as the surrounding text.
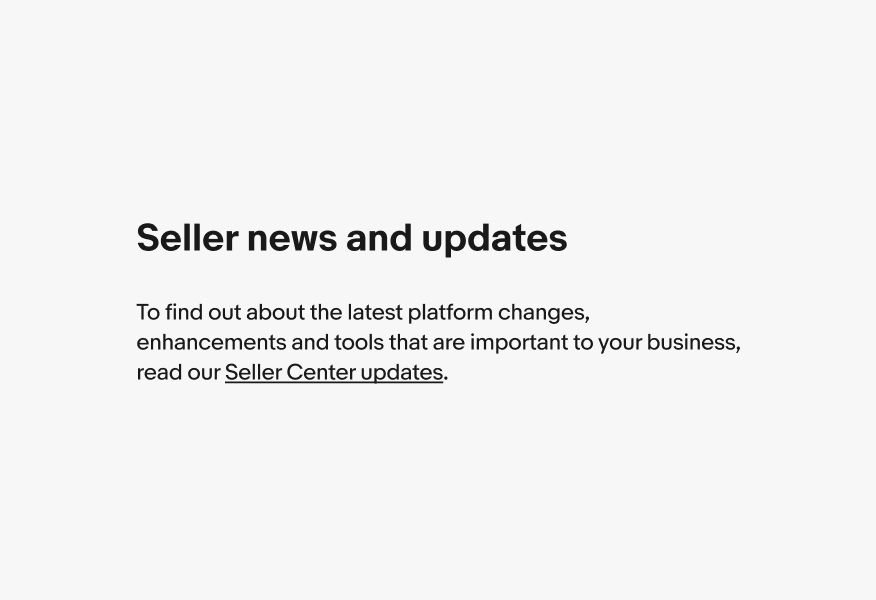
Don’t mix type sizes.
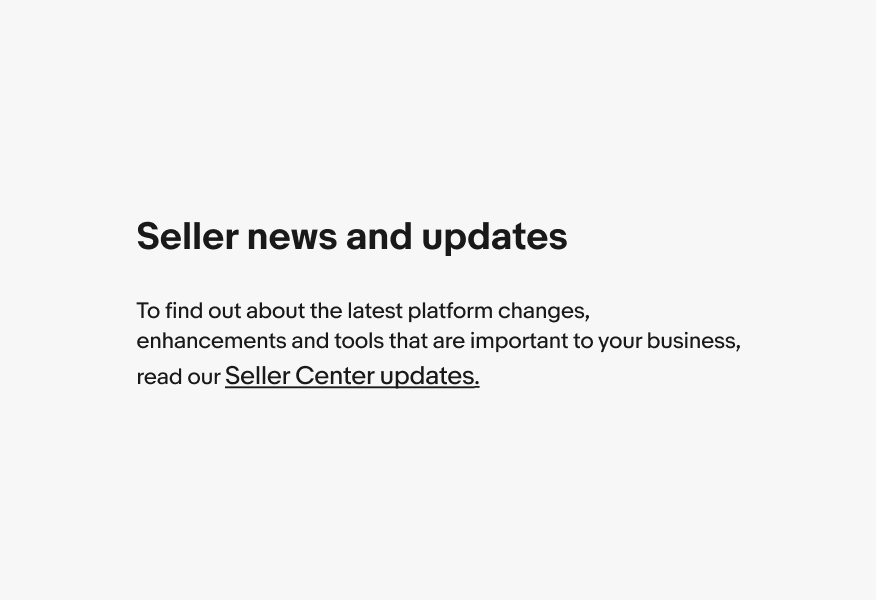
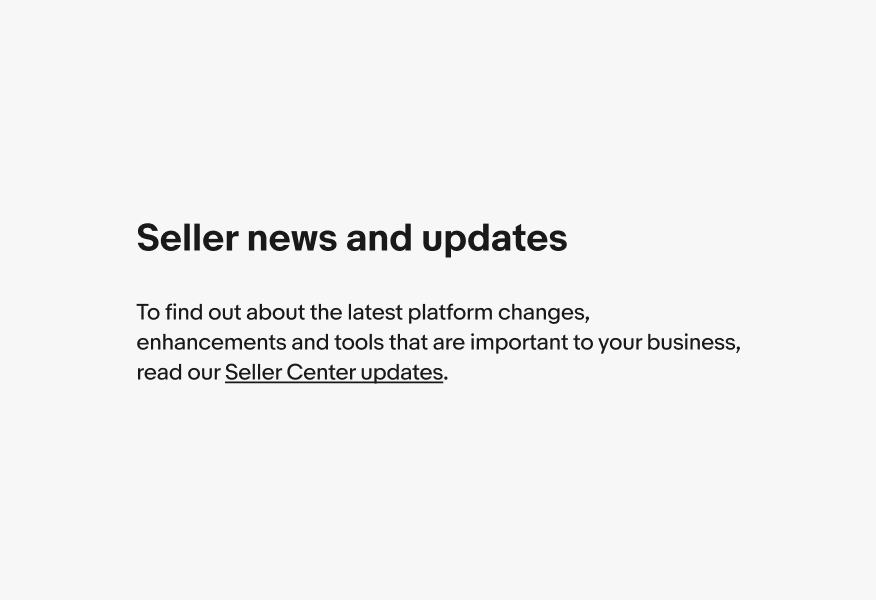
Titles
Use links in body copy or footnotes.
Don’t use links for titles or headlines.
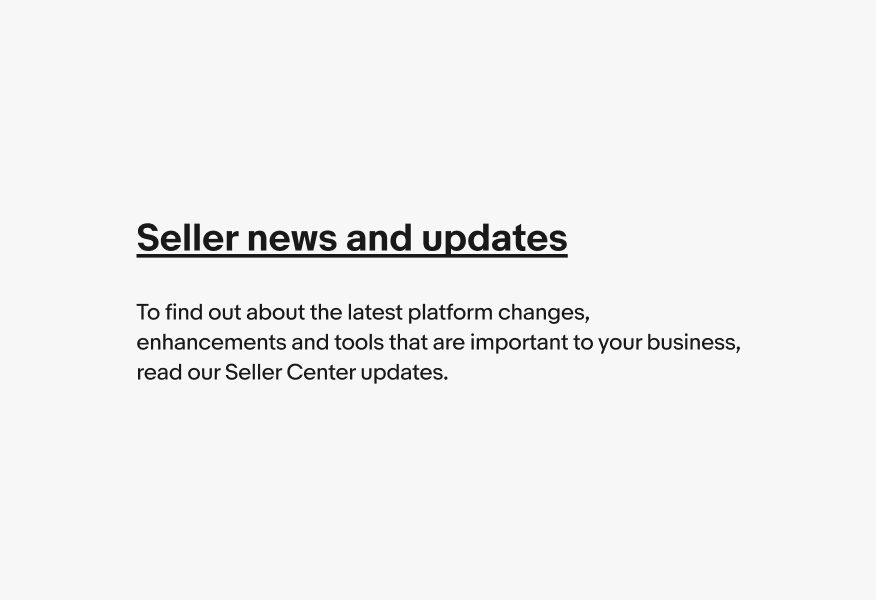
Browser window
Do open links in the same browser window.
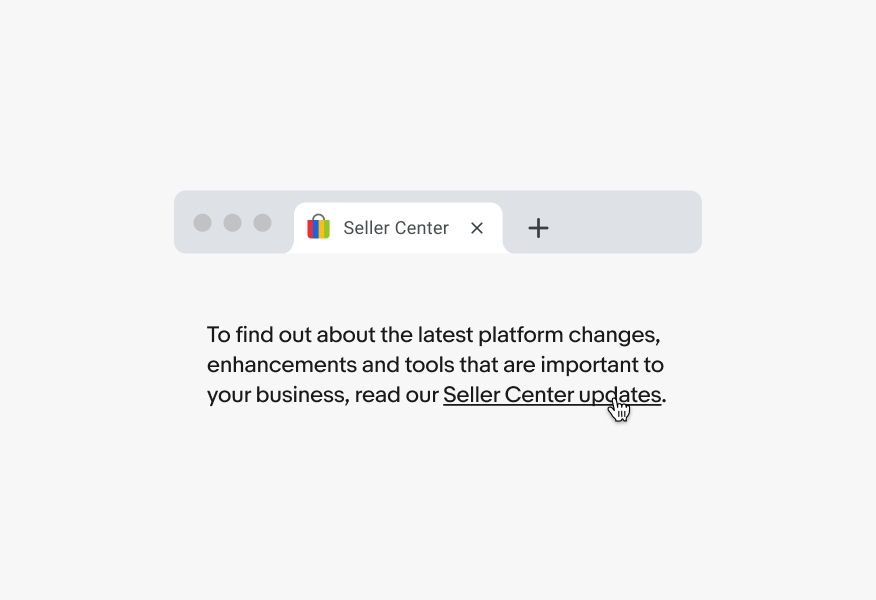
Don’t force links to open in a new window. This is a poor experience because it takes control away from the user and forces web-browsing behavior upon them.
Legal links
Do use text links for non-legal links, such as Seller policy. Use blue links when required for legal compliance.
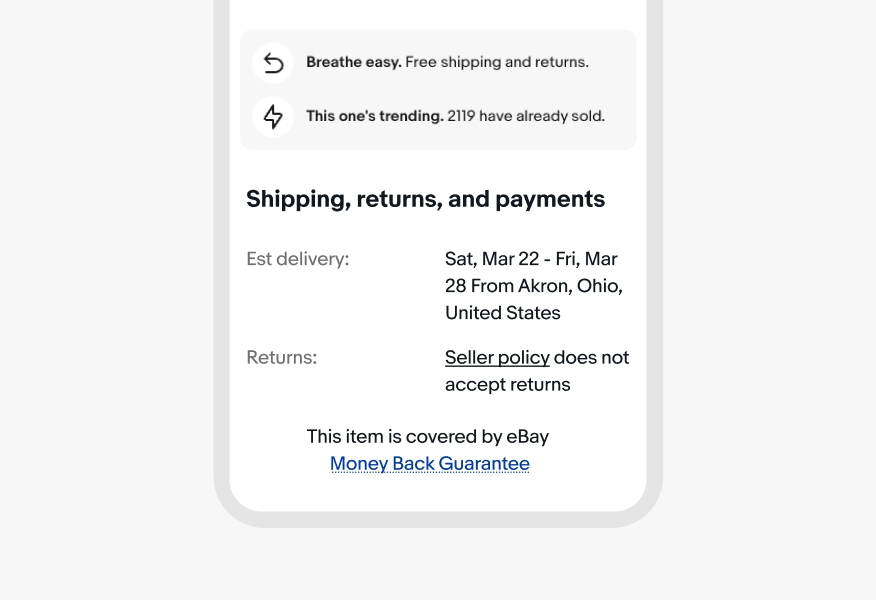
Don’t use blue for non-legal links, such as Seller policy.